Design and Finite Element Analysis of a Portable Bus Service Ramp to Reduce Dependence on Service Pits
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.21831/jamat.v2i2.2479Keywords:
DMADV, Finite Element Analysis, Bus Repair, Portable RampAbstract
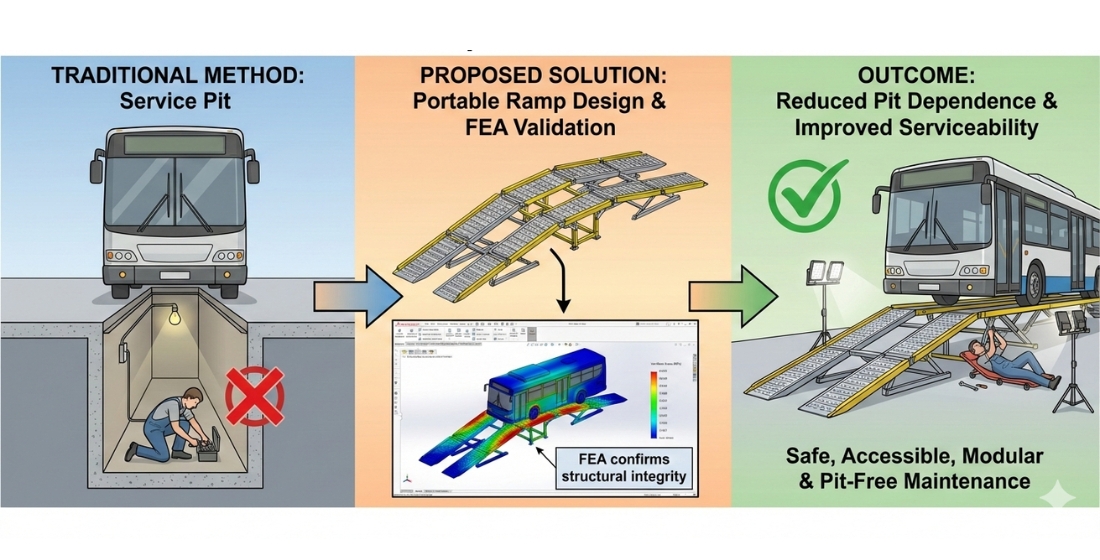
This study aims to: (1) design and analyze a portable ramp to improve bus repair efficiency at PT. United Tractors Semarang Branch, (2) with a focus on facilitating repairs and reducing dependence on service pits. (3) This portable ramp is expected to overcome access constraints to the underside of buses, speed up repair time, and improve work safety for mechanics. This study uses the DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Verify) method to develop portable ramps. These stages include problem discovery, technical data collection, analysis of materials, 3D model design using SolidWorks, and verification using Finite Element Analysis (FEA) to ensure structural strength and compliance with safety standards. This study successfully designed and analyzed a portable ramp for bus repairs, capable of withstanding an operational load of 88,750 Newtons with a safety factor≥ 3.0, a maximum deformation of ≤ 5 mm, and a safe von Mises stress distribution. The selection of ASTM A36 Carbon Steel resulted in optimal strength and weight, as well as cost efficiency. The ramp design also meets workshop operational needs and improves repair process efficiency. This research successfully designed an optimal portable ramp for the PT. United Tractors Semarang Branch Workshop, considering operational efficiency and safety, ASTM A36 Carbon Steel was selected as the best material based on strength, weight, and cost. It is recommended to implement this portable ramp, along with technician training, maintenance system development, and expansion to other branches, to improve bus repair efficiency.
Downloads
References
[1] Y. O. Susilo, W. Santosa, T. B. Joewono, and D. Parikesit, “A reflection of motorization and public transport in Jakarta metropolitan area,” IATSS research, vol. 31, no. 1, pp. 59–68, 2007.
[2] M. Z. SYIFA, “LAPORAN MAGANG II PERBAIKAN DAN PEMELIHARAAN ARMADA SUROBOYO BUS,” 2025.
[3] A. Shofia, R. M. Putri, S. Salsabila, M. Perwasih, R. Yani, and H. Domila, “Analisis postur kerja dengan metode RULA pada bagian pengemasan di CV Tani Makmur Sejahtera Bersama Tbk, Kota Padang,” Jurnal Teknik Industri Terintegrasi, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 1518–1524, 2025.
[4] I. Rahela and A. Ismail, “Pengukuran dan Evaluasi Safety Culture Maturity Level pada Kegiatan Service dan Perawatan Alat Berat di PT United Tractors (Studi Kasus: PT United Tractors Tbk, Semarang),” 2023.
[5] I. M. Suartika, K. A. Kristiawan, Z. Arifin, S. F. Mustaqim, and B. Istiyanto, “Pelaksanaan Pemeriksaan Kendaraan Asset serta Peningkatan Corporate Communication di United Tractors Semarang,” Jurnal Abdimas Transjaya, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 76–88, 2023, doi: 10.46447/jat.v1i1.579.
[6] F. Trapsilawati, “Seminar nasional Teknik Industri 2019 UNIVERSITAS GADJAH MADA,” 2019.
[7] H. Maksum and W. Purwanto, Sistem Kemudi, Rem dan Suspensi. UNP PRESS, 2021.
[8] J. Pengabdian Masyarakat et al., “PIMAS Perbaikan Posisi Dan Postur Pekerja Pada Mekanik Bengkel Mobil,” Jurnal Pengabdian Masyarakat (PIMAS), vol. 3, no. 3, 2024, doi: 10.35960/pimas.v3i3.1462.
[9] T. Storr, J. Spicer, P. Frost, S. Attfield, C. D. Ward, and L. L. Pinnington, “Design features of portable wheelchair ramps and their implications for curb and vehicle access.,” J Rehabil Res Dev, vol. 41, 2004.
[10] B. W. Lenggana, A. Nugroho, and U. Ubaidillah, “Structural simulation of wheelchair ramp using finite element method,” Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science and Technology (JMEST), vol. 8, no. 2, p. 6, 2024.
[11] F. Giudice, S. Missori, C. Scolaro, and A. Sili, “A review on metallurgical issues in the production and welding processes of clad steels,” Materials, vol. 17, no. 17, p. 4420, 2024.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Automotive and Mechanical Applied Technology

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This journal is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
You are free to: Share (copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format) and Adapt (remix, transform, and build upon the material) for any purpose, even commercially, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source.











