- Focus and Scope
- Section Policies
- Peer Review Process
- Publication Ethics and Malpractice Statement
- Journal Subscription
- Open Access Policy
Focus and Scope
JDVTM covers all topics related to technical vocational education and training (TVET) on mechanical engineering with topic areas are as follows:
- TVET Learning theories and strategies
- TVET Management and policy
- TVET evaluation and assessment
- TVET Applied technology
- Vocational career development
- TVET Teachers' and trainers' professional development
Section Policies
Articles
Editorial
Peer Review Process
Editorial Team’s will do plagiarism scanning for all of the articles submitted to this journal by using Google Scholar and Anti-Plagiarism Application. Then the articles also will be reviewed will be reviewed by at least two anonymous reviewers (Single-Blind Review). Finally, Editorial Team’s will make a decision for the articles submitted that accepted or no based on the result of plagiarism scanning and the suggestions from the reviewers.
Publication Ethics and Malpractice Statement
Jurnal Dinamika Vokasional Teknik Mesin is committed to upholding the highest standards of publication ethics and takes all possible measures against any publication malpractices. The Editorial Board is responsible for, among others, preventing publication malpractice. Unethical behavior is unacceptable, and this journal does not tolerate plagiarism in any form. Authors who submitted articles: affirm that manuscript contents are original. Furthermore, the authors’ submission also implies that the manuscript has not been published previously in any language, either wholly or partly, and is not currently submitted for publication elsewhere. Editors, authors, and reviewers, within the International Journal of Advances in Intelligent Informatics, are to be fully committed to good publication practice and accept the responsibility for fulfilling the following duties and responsibilities, as set by the COPE Code of Conduct for Journal Editors. As part of the Core Practices, COPE has written guidelines on the http://publicationethics.org/resources/guidelines.
Section A: Publication and authorship
- All submitted papers are subject to a strict peer-review process by reviewers that are experts in the area of the particular manuscript.
- The review process is double-blind peer-review.
- The factors that are taken into account in review are relevance, soundness, significance, originality, readability, and language.
- The possible decisions include acceptance, acceptance with revisions, or rejection.
- If authors are encouraged to revise and resubmit a submission, there is no guarantee that the revised submission will be accepted.
- Rejected articles will not be re-reviewed.
- The paper acceptance is constrained by such legal requirements as shall then be in force regarding libel, copyright infringement, and plagiarism.
- No research can be included in more than one publication.
Section B: Authors’ responsibilities
- Authors must certify that their manuscripts are their original work.
- Authors must certify that the manuscript has not previously been published elsewhere.
- Authors must certify that the manuscript is not currently being considered for publication elsewhere.
- The authors must participate in the peer-review process.
- Authors are obliged to provide retractions or corrections of mistakes.
- All Authors mentioned in the paper must have significantly contributed to the research.
- The authors must state that all data in the paper are real and authentic.
- The authors must notify the Editors of any conflicts of interest.
- The authors must identify all sources used in the creation of their manuscript.
- Authors must report any errors they discover in their published paper to the Editors.
Section C: Reviewers’ responsibilities
- Reviewers should keep all information regarding papers confidential and treat them as privileged information.
- Reviews should be conducted objectively, with no personal criticism of the author.
- Reviewers should express their views clearly with supporting arguments.
- Reviewers should identify relevant published work that has not been cited by the authors.
- Reviewers should also call to the Editor in Chief’s attention any substantial similarity or overlap between the manuscript under consideration and any other published paper of which they have personal knowledge.
- Reviewers should not review manuscripts in which they have conflicts of interest resulting from competitive, collaborative, or other relationships or connections with any of the authors, companies, or institutions connected to the papers.
Section D: Editors’ responsibilities
- Editors have complete responsibility and authority to reject/accept an article.
- Editors are responsible for the contents and overall quality of the publication.
- Editors should always consider the needs of the authors and the readers when attempting to improve the publication.
- Editors should guarantee the quality of the papers and the integrity of the academic record.
- Editors should publish errata pages or make corrections when needed.
- Editors should have a clear picture of research funding sources.
- Editors should base their decisions solely one the papers’ importance, originality, clarity, and relevance to the publication’s scope.
- Editors should not reverse their decisions nor overturn the ones of previous editors without serious reason.
- Editors should preserve the anonymity of reviewers.
- Editors should ensure that all research material they publish conforms to internationally accepted ethical guidelines.
- Editors should only accept a paper when reasonably certain.
- Editors should act if they suspect misconduct, whether a paper is published or unpublished, and make all reasonable attempts to persist in obtaining a resolution to the problem.
- Editors should not reject papers based on suspicions; they should have proof of misconduct.
- Editors should not allow any conflicts of interest between staff, authors, reviewers, and board members.
Retraction
The papers published in the JDVTM will be considered to retract in the publication if :
- They have clear evidence that the findings are unreliable, either as a result of misconduct (e.g., data fabrication) or honest error (e.g., miscalculation or experimental error)
- the findings have previously been published elsewhere without proper crossreferencing, permission or justification (i.e., cases of redundant publication)
- it constitutes plagiarism
- it reports unethical research
The mechanism of retraction follows the Retraction Guidelines of the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE), which can be accessed at https://publicationethics.org/files/retraction%20guidelines.pdf.
Journal Subscription
Jurnal Dinamika Vocational Teknik Mesin can be purchased by CASH or BANK TRANSFER. The price for one issue is IDR 300.000,- (excludes shipment cost).
Furthermore information please contact to Surono by sending an email to journal_dinamika@uny.ac.id, or visit Journal Manager office on the Jurusan Pendidikan Teknik Mesin Fakultas Teknik Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta.
Open Access Policy
This journal is open access journal which means that all content is freely available without charge to users or / institution. Users are allowed to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to full text articles in this journal without asking prior permission from the publisher or author. This is in accordance with Budapest Open Access Initiative
Budapest Open Access Initiative
For various reasons, this kind of free and unrestricted online availability, which we will call open access, has so far been limited to small portions of the journal literature. But even in these limited collections, many different initiatives have shown that open access is economically feasible, that it gives readers extraordinary power to find and make use of relevant literature, and that it gives authors and their works vast and measurable new visibility, readership, and impact. To secure these benefits for all, we call on all interested institutions and individuals to help open up access to the rest of this literature and remove the barriers, especially the price barriers, that stand in the way. The more who join the effort to advance this cause, the sooner we will all enjoy the benefits of open access.
The literature that should be freely accessible online is that which scholars give to the world without expectation of payment. Primarily, this category encompasses their peer-reviewed journal articles, but it also includes any unreviewed preprints that they might wish to put online for comment or to alert colleagues to important research findings. There are many degrees and kinds of wider and easier access to this literature. By "open access" to this literature, we mean its free availability on the public internet, permitting any users to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of these articles, crawl them for indexing, pass them as data to software, or use them for any other lawful purpose, without financial, legal, or technical barriers other than those inseparable from gaining access to the internet itself. The only constraint on reproduction and distribution, and the only role for copyright in this domain, should be to give authors control over the integrity of their work and the right to be properly acknowledged and cited.
While the peer-reviewed journal literature should be accessible online without cost to readers, it is not costless to produce. However, experiments show that the overall costs of providing open access to this literature are far lower than the costs of traditional forms of dissemination. With such an opportunity to save money and expand the scope of dissemination at the same time, there is today a strong incentive for professional associations, universities, libraries, foundations, and others to embrace open access as a means of advancing their missions. Achieving open access will require new cost recovery models and financing mechanisms, but the significantly lower overall cost of dissemination is a reason to be confident that the goal is attainable and not merely preferable or utopian.
To achieve open access to scholarly journal literature, we recommend two complementary strategies.
I. Self-Archiving: First, scholars need the tools and assistance to deposit their refereed journal articles in open electronic archives, a practice commonly called, self-archiving. When these archives conform to standards created by the Open Archives Initiative, then search engines and other tools can treat the separate archives as one. Users then need not know which archives exist or where they are located in order to find and make use of their contents.
II. Open-access Journals: Second, scholars need the means to launch a new generation of journals committed to open access, and to help existing journals that elect to make the transition to open access. Because journal articles should be disseminated as widely as possible, these new journals will no longer invoke copyright to restrict access to and use of the material they publish. Instead they will use copyright and other tools to ensure permanent open access to all the articles they publish. Because price is a barrier to access, these new journals will not charge subscription or access fees, and will turn to other methods for covering their expenses. There are many alternative sources of funds for this purpose, including the foundations and governments that fund research, the universities and laboratories that employ researchers, endowments set up by discipline or institution, friends of the cause of open access, profits from the sale of add-ons to the basic texts, funds freed up by the demise or cancellation of journals charging traditional subscription or access fees, or even contributions from the researchers themselves. There is no need to favor one of these solutions over the others for all disciplines or nations, and no need to stop looking for other, creative alternatives.
Open access to peer-reviewed journal literature is the goal. Self-archiving (I.) and a new generation of open-access journals (II.) are the ways to attain this goal. They are not only direct and effective means to this end, they are within the reach of scholars themselves, immediately, and need not wait on changes brought about by markets or legislation. While we endorse the two strategies just outlined, we also encourage experimentation with further ways to make the transition from the present methods of dissemination to open access. Flexibility, experimentation, and adaptation to local circumstances are the best ways to assure that progress in diverse settings will be rapid, secure, and long-lived.
The Open Society Institute, the foundation network founded by philanthropist George Soros, is committed to providing initial help and funding to realize this goal. It will use its resources and influence to extend and promote institutional self-archiving, to launch new open-access journals, and to help an open-access journal system become economically self-sustaining. While the Open Society Institute's commitment and resources are substantial, this initiative is very much in need of other organizations to lend their effort and resources.
We invite governments, universities, libraries, journal editors, publishers, foundations, learned societies, professional associations, and individual scholars who share our vision to join us in the task of removing the barriers to open access and building a future in which research and education in every part of the world are that much more free to flourish.
February 14, 2002
Budapest, Hungary
Leslie Chan: Bioline International
Darius Cuplinskas: Director, Information Program, Open Society Institute
Michael Eisen: Public Library of Science
Fred Friend: Director Scholarly Communication, University College London
Yana Genova: Next Page Foundation
Jean-Claude Guédon: University of Montreal
Melissa Hagemann: Program Officer, Information Program, Open Society Institute
Stevan Harnad: Professor of Cognitive Science, University of Southampton, Universite du Quebec a Montreal
Rick Johnson: Director, Scholarly Publishing and Academic Resources Coalition (SPARC)
Rima Kupryte: Open Society Institute
Manfredi La Manna: Electronic Society for Social Scientists
István Rév: Open Society Institute, Open Society Archives
Monika Segbert: eIFL Project consultant
Sidnei de Souza: Informatics Director at CRIA, Bioline International
Peter Suber: Professor of Philosophy, Earlham College & The Free Online Scholarship Newsletter
Jan Velterop: Publisher, BioMed Central

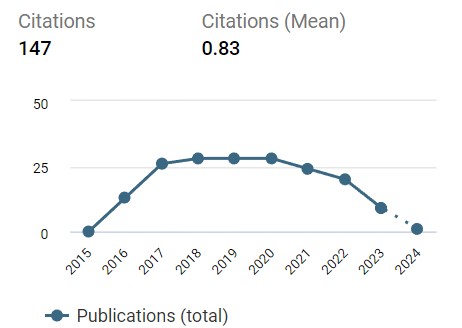

.jpg)



