Implementation of Low-Cost Smart Waste Bin with Fuzzy Logic Control Using MQ-2 and HY-SRF05
Downloads
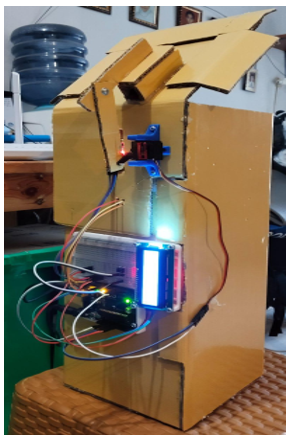
Urban waste management systems often fail to address hygiene and efficiency when relying on conventional bins or rigid threshold-based controllers. This paper presents a low-cost smart trash bin that integrates dual-sensor fuzzy logic control to adaptively regulate lid positions in real time. Unlike prior designs dependent on a single sensing modality, the proposed system fuses odor intensity (via MQ-2 gas sensor) and fill-level data (via HY-SRF05 ultrasonic sensor) within a Sugeno-type fuzzy inference framework. The controller supports five graded lid positions, ranging from fully closed to fully open, ensuring nuanced and hygienic responses to varying environmental conditions. Experimental validation across 25 scenarios yielded robust performance, with maximum errors below 9% and an average deviation of only 1.91%. The most accurate results were observed in the fully closed state, while the highest deviations occurred in the almost closed position due to mechanical limitations and nonlinear actuator behavior. Despite these drawbacks, the system consistently demonstrated adaptive decision-making and stable operation, confirming its suitability for real-world applications. Furthermore, comparative analysis against threshold-based and AI-based controllers reveals that the fuzzy approach achieves superior adaptability and near-ANN accuracy while maintaining computational efficiency compatible with Arduino-based platforms. These findings establish fuzzy sensor fusion as a practical pathway toward sustainable, IoT-enabled, and educationally relevant waste management solutions, paving the way for integration into future smart city infrastructures
Downloads
[1] E. de Titto and A. Savino, “Human Health Impact of Municipal Solid Waste Mismanage-ment: A Review,” Advances in Environmental Engineering Research, vol. 5, no. 2, p. 014, Jun. 2024. DOI: 10.21926/aeer.2402014.
[2] A. Rahman, N. L. Dewi, and Y. Prabowo, “Urban Waste Management Challenges and IoT-Based Solutions,” Smart Cities Journal, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 45–54, 2021.
[3] R. Kumar, A. Das, and M. Roy, “Smart Waste Bin Management Using Fuzzy Logic Con-troller,” Journal of Environmental Engineering, vol. 147, no. 4, pp. 110–118, 2021.
[4] D. A. Prasetyo and F. Lestari, “Hybrid Fuzzy Control System for Hazardous Waste Detec-tion in Smart Bins,” Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Informatics, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 78–86, 2025.
[5] H. Zhang, Y. Liu, and W. Chen, “Design of Intelligent Waste Monitoring System Using Ul-trasonic and Gas Sensors,” IEEE Sensors Journal, vol. 22, no. 11, pp. 10349–10357, 2022.
[6] R. Setiawan and B. Nugroho, “Fuzzy Logic-Based Automation System for Environmental Monitoring,” TELKOMNIKA, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 11–19, 2023.
[7] S. Prasetyo and L. Lestari, “Hybrid fuzzy control for gas–ultrasonic smart bin applica-tions,” Journal of Electrical Engineering and Automation, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 33–42, 2023
[8] M. Ikram et al., “Artificial neural network–based smart waste bin for urban management,” IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp. 155210–155222, 2023
[9] J. Guo, “IoT Technology in Urban Waste Management: Smart Waste Bin Systems”, HSET, vol. 111, pp. 452–458, Aug. 2024
[10] A. Wijaya, R. Sari, and M. Taufiq, “Real-Time Gas Detection for Smart Environments Us-ing MQ Series Sensors,” Indonesian Journal of Electronics and Instrumentation Systems, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 12–20, 2024.
[11] A. Tong et al., “Application Smart Dustbin With IoT: Tspintar,” Applied Information Technology and Computer Science, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 514–528, 2022.
[12] A. Davis and D. Dukes, “Adaptive Fuzzy Logic for Environmental Monitoring: A Review,” Science of The Total Environment, vol. 883, p. 163639, 2023.
[13] F. Furizal, A. Ma’arif, S. A. Wijaya, M. Murni, and I. Suwarno, “Analysis and Performance Comparison of Fuzzy Inference Systems in Handling Uncertainty: A Review,” Journal of Robotics and Control (JRC), vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 1203–1215, Jun. 2024.
[14] M. Malik and A. Prasetyo, “Design a Smart Trash Using Fuzzy Logic Algorithm,” in Proc. ICSET, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 9–17, 2022.
[15] D. S. Nugroho, S. Rosad, and N. Agustin, “Real Time Smart Trash Bins Monitoring System Using Fuzzy Logic Method in Kuripan Village,” INISTA Journal, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 70–79, 2023.
[16] S. T. Ikram, V. Mohanraj, S. Ramachandran, and A. Balakrishnan, “An Intelligent Waste Management Application Using IoT and a Genetic Algorithm–Fuzzy Inference System,” Applied Sciences, vol. 13, no. 6, p. 3943, 2023.
[17] W. A. Purnomo and R. Efendi, “Smart Trash System: IoT Innovation in Sustainable Or-ganic Waste Management Based on Zero Waste,” International Journal of Technology Vocational Education and Training, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 65–69, Dec. 2024.
[18] Lam, K.N., Huynh, N.H., Ngoc, N.B., Nhu, T.T.H., Thao, N.T., Hao, P.H., Kiet, V.V., Huynh, B.X. and Kalita, J. (2021). Using Artificial Intelligence and IoT for Constructing a Smart Trash Bin. Future Data and Security Engineering. Big Data, Security and Privacy, Smart City and Industry 4.0 Applications, [online] pp.427–435.
[19] F. Furizal et al., “Analysis and Performance Comparison of Fuzzy Inference Systems in Handling Uncertainty: A Review,” Journal of Robotics and Control (JRC), vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 1203–1215, 2024.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The Authors submitting a manuscript do so on the understanding that if accepted for publication, copyright publishing of the article shall be assigned to Journal.



















